What is TFT LCD Display And Modules?
In today's digital age, TFT LCD displays have become ubiquitous in our everyday lives, from smartphones and tablets to computer monitors and televisions. But what exactly is a TFT LCD display, and how does it work? Let's dive into the world of TFT LCD technology to gain a better understanding of this essential component of modern electronics.
Brief History of TFT LCDs
- 1957 – John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET.
- 1992 – Paul K. Weimer of RCA leveraged Wallmark’s patent and developed thin-film transistor technology (TFT).
- 1968 – Bernard Lechner of RCA implemented TFT technology in the liquid-crystal display (LCD) for the first time
- 1971 – Lechner, F. J. Marlowe, E. O. Nester, and J. Tults demonstrated a 2-by-18 matrix display driven by a hybrid circuit using the dynamic scattering mode of LCDs
- 1974 – Brody and Fang-Chen Luo demonstrated the first flat active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) using CdSe TFTs,
- 1975 – Brody coined the term “active matrix LCDs”,
- 2020 – TFT LCD display technology dominants the display market now. Within the last 20 years, it has wiped out the market of CRT (cathode-ray tube) and Plasma. The only challenges are OLED (organic light-emitting diode)and Micro LED (Maybe, still in lab).
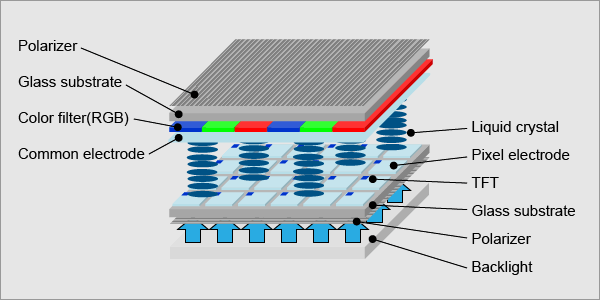
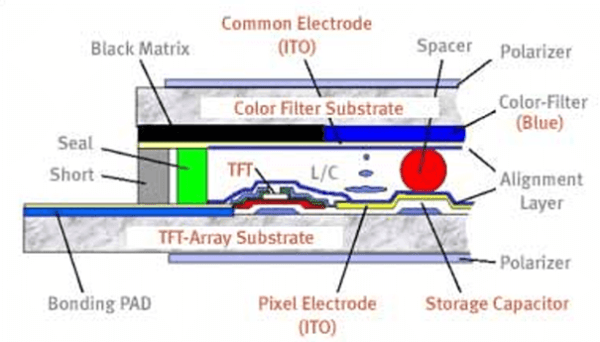
TFT LCD, which stands for Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display, A type of LCD flat panel display screen in which each pixel is controlled by one to four transistors. The TFT technology provides the best resolution of all the flat panel techniques, but it is also the most expensive. TFT screens are sometimes called active matrix LCDs.That uses thin-film transistor technology to improve image quality and provide better performance compared to traditional LCD displays. The TFT technology allows for each pixel on the display to be controlled individually, resulting in sharper images, faster response times, and improved color accuracy.
At the heart of a TFT LCD display is a liquid crystal layer sandwiched between two transparent electrodes. When an electric current is applied to the electrodes, the liquid crystal molecules align to control the passage of light through the display. The thin-film transistors act as switches, regulating the amount of charge sent to each pixel and determining the color and brightness of the displayed image.
One of the key advantages of TFT LCD displays is their ability to produce vibrant colors and high-resolution images, making them ideal for applications that require precise visual representation, such as graphic design, gaming, and video playback. Additionally, TFT LCD displays are known for their energy efficiency, as they consume less power compared to other display technologies, making them popular choices for portable devices like smartphones and laptops.
TFT LCD displays come in various types, including twisted nematic (TN), in-plane switching (IPS), and advanced fringe field switching (AFFS), each offering unique benefits in terms of viewing angles, color accuracy, and response times. Manufacturers continue to innovate in TFT LCD technology, pushing the boundaries of display quality and performance to meet the demands of today's tech-savvy consumers.
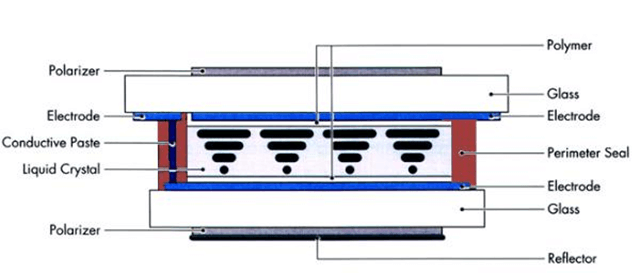 Monochrome Passive LCD Display
Monochrome Passive LCD Display
TFT LCDs offer several advantages over other types of displays (CRT, Plasma). It is light, thin, and energy efficient which made mobile phones, laptops, hang-on wall LCD TV, flat computer monitors and other handhold devices possible. TFT LCD Monitor are also relatively inexpensive, which makes it dominant in display world.
When we say type of LCD, we mean two kinds of LCDs: Active TFT color display and Monochrome passive display. Before TFT display was invented, the world used passive matrix lcd for many years. Passive matrix LCD can only be used for monochrome displays like calculators, watches (not iWatch), thermostats (not Nest), utility meters etc. Thanks to TFT LCD, the world is more colorful.