How to Choose the Best Mounting For Your Channel Letters?
Metal Fabrication Channel Letter Signages are common signs in stores, office buildings, and other commercial spaces, and they attract attention with their unique design and bright illumination.
However, proper installation is essential to ensure that these signs are securely mounted in the desired location and remain stable over time.


- Consider Location and Environment
Before choosing a mounting method, it is crucial to consider the location and surroundings of the sign. While Outdoor Signages need to withstand the elements and other natural elements, Indoor Signages may face different challenges. Therefore, the mounting method chosen must be able to adapt to these conditions.
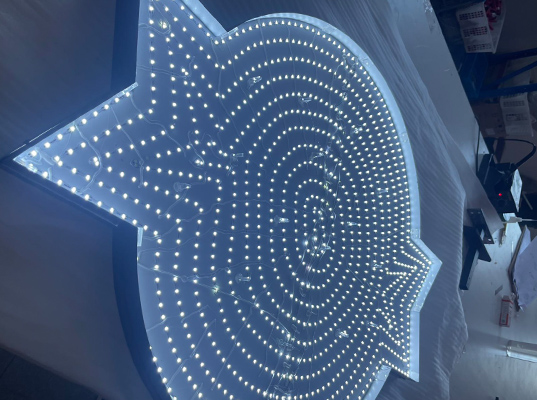
Additionally if your sign is a back-lit type, like Backlit Metal Channel Letter Signages then an overhanging mount is the perfect way to maximize the sign's backlit features. If your sign is front illuminated, Satinsign staff will usually recommend that you choose expansion screws to secure individual letters or logos, depending on the weight of the individual letters.
- Evaluate Building Structure
Evaluate building structure to determine suitable mounting points and methods. The wall material, the flatness of the wall, and the available support structure will all influence the selection of the best mounting method.
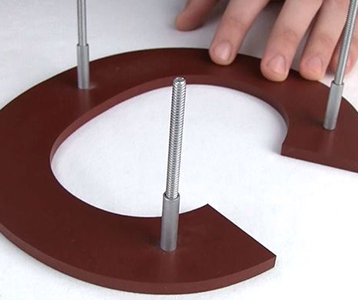
If you want to mount your sign on a concrete wall, expansion screws or wire rods are the safest way to go. If you are mounting on a metal backing, the mounting method depends on the thickness of the metal, if it is more than 5cm, we recommend 10cm screws, and Satinsign will provide you with these mounting accessories free of charge!
- Consult with Professionals
If you are confused or unsure about the best installation method, consult with professionals. A sign manufacturer or installation specialist can advise you on the best installation method and ensure that your channel letters are safely and securely mounted in the proper location.
Satinsign has 13 years of signage making experience, we not only provide free mounting accessories, 1:1 paper mounting scripts, but also all the accessories meet the local sign inspection standards, absolutely safe and reliable.
Welcome to browse our website for more customized installation services about wholesale channel letter signs!